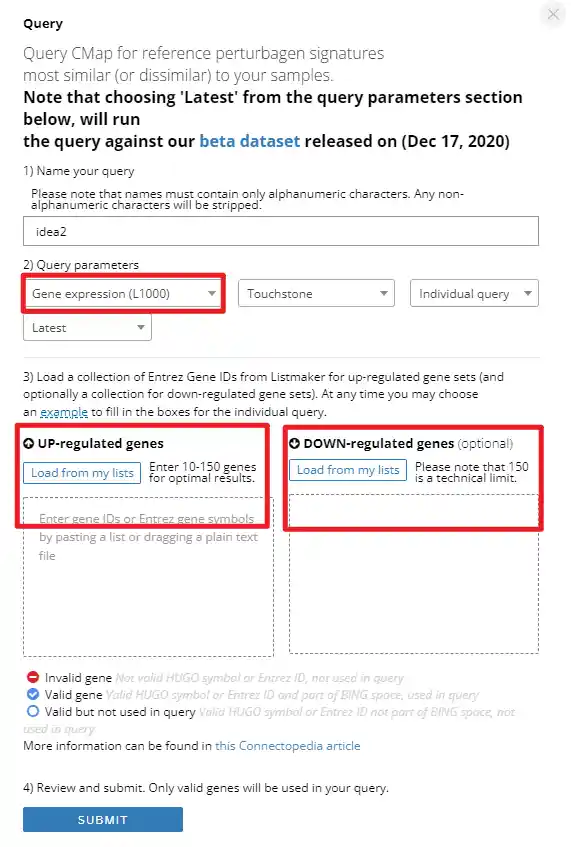
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| library(ComplexHeatmap)
library(circlize)
col_fun <- colorRamp2(
c(-1, 0, 1),
c("#BC3C29AA", "white", "#99CCCCAA")
)
test <- cmap[c('pert_iname', 'cell_iname', 'tas', 'raw_cs', 'fdr_q_nlog10')]
test$fdr_q_nlog10 <- as.numeric(test$fdr_q_nlog10)
test$raw_cs <- as.numeric(test$raw_cs)
test <- subset(test, cell_iname %in% c('LNCAP', 'PC3', 'VCAP'))
mat <- f_long2wide(tail(test, 20), 'cell_iname', 'pert_iname', 'raw_cs')
mat_tmp <- f_long2wide(test, 'cell_iname', 'pert_iname', 'raw_cs')
mat <- mat_tmp[rownames(mat),]
mat[is.nan(mat)] <- 0
options(repr.plot.width=4, repr.plot.height=5)
Heatmap(mat, col=col_fun, name = 'raw_cs', row_order=nrow(mat):1, column_order = 1:3)
|